Considered one of the ocean’s most fascinating creatures, the blue-ringed octopus is noted for its stunning blue rings, which appear when it feels threatened. But these apparent warning signs are more than just a beautiful addition to our coral reefs and other coastal areas; they carry with them dangerous amounts of venom – enough to kill 26 grown men in minutes! Despite their powerful toxicity, these octopuses remain important to marine life. In this blog post, we’ll explore some interesting facts about blue-ringed octopuses and get a better understanding of why they exist and how they benefit us, humans.
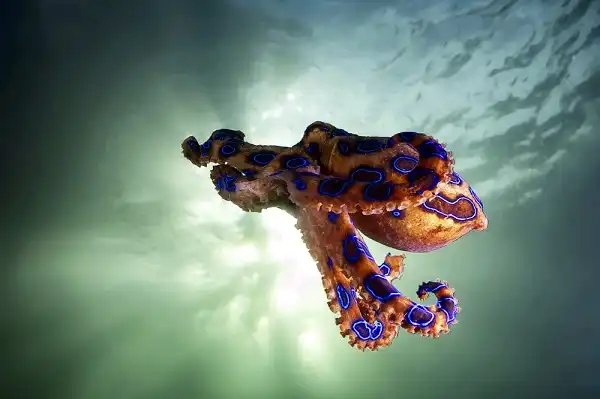
Blue-Ringed Octopus Description
The blue-ringed octopus, or Hapalochlaena lunulata, is found in coastal regions of the Indian and Pacific oceans. Most notably, it can be found among coral reefs and areas with rocks, rubble, and sand. The most distinguishing feature of this species is the bright blue circles on its body with bright yellow centers. Apart from its toxicity, the blue-ringed octopus also stands out for its unique hunting style; rather than using tentacles to catch prey as other octopuses do, this species uses its venomous bite! They use their mouths as a sort of “fishing rod”, and can even inject poison into their prey.
Blue-Ringed Octopus Habitat
The Blue-Ringed Octopus is found in warm coastal waters ranging from the Indian Ocean to the Pacific Ocean, particularly around Australia, Japan, and New Zealand. Generally, they prefer shallow coral reefs and rocky bottoms where they can find plenty of hiding spots among rocks and crevices. Blue-ringed octopuses are able to regulate their buoyancy levels by controlling the amount of water present in their bodies – a unique trait that allows them to move up or down in the water column.
They are also known to be highly territorial; males will often create small territories with boundaries underwater, which they defend from intruders. To survive in the wild, blue-ringed octopuses must stay hidden from predators during daylight and hunt for prey at night. During this time, they use their excellent sensory organs (such as smell) to locate potential meals before swiftly capturing them with their tentacles. Overall, blue-ringed octopuses inhabit a wide range of habitats across tropical regions of the world’s oceans and are an important species within marine ecosystems. These incredible creatures play both predator and prey roles depending on their environment; without them, our coral reefs would be drastically different!
Blue-Ringed Octopus Diet
The Blue-Ringed Octopus has a diverse diet in order to survive in its natural habitat. They are opportunistic feeders, meaning that they will take advantage of whatever food is available to them. The primary sources of prey include shrimp, crabs, small fish, sea slugs, snails, and other invertebrates. In addition to their carnivorous meals, blue-ringed octopuses also feed on algae, plankton, and other debris that settle from the ocean onto their habitat. This allows them to maintain good health while staying in one place for long periods of time.
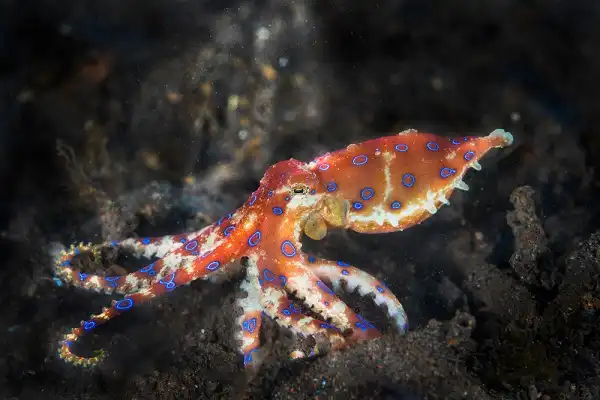

Blue-Ringed Octopus Size
The Blue-Ringed Octopus is a relatively small cephalopod species, with an average size of 6-8 inches in length. However, they can grow up to 12 inches in length, and weigh up to 3.5 ounces. Their tentacles are lined with hundreds of suckers that help them grip prey and navigate their environment. They are known as one of the smallest octopus species in the world, but their venomous bite makes them incredibly dangerous predators. Despite their small size, these creatures can deliver a powerful dose of poison to any potential threats – including humans!
Blue-Ringed Octopus Lifespan
The Blue-Ringed Octopus has an average lifespan of five years, though some individuals have been known to live longer. Generally, the octopuses reach their full size within two years and reproduce during their third or fourth year of life. After mating, most blue-ringed octopuses will die shortly after laying eggs. In the wild, factors such as predation and environmental conditions can influence the lifespan of a blue-ringed octopus. Predators such as fish, crabs, and sea birds will often feed on them despite their venomous bite. In addition, natural disasters like storms and hurricanes can sweep away entire colonies of these creatures in a matter of moments. In captivity, blue-ringed octopuses can survive for longer periods of time if given the proper care. This includes providing them a warm temperature (77–82°F) and plenty of food sources such as shrimp and crabs. If well taken care of, these fascinating creatures could live for up to eight years in captivity!
Blue-Ringed Octopus Behavior
The Blue-Ringed Octopus is a highly intelligent and social creature that has many unique behaviors. These creatures display an array of communication tactics, such as changing their body color in order to transmit messages or warnings to other octopuses in their environment. They are known for their vibrant coloration, which can range from yellow to red, depending on their mood. This color change can act as a warning sign when the octopus feels threatened by predators or other large animals. These creatures also use ink clouds to escape from danger; when threatened, they will emit a dark cloud of ink in order to confuse and distract their predator so that it can make their escape! In addition to these defensive behaviors, blue-ringed octopuses are also capable of learning new behaviors over time. They have been observed recognizing different predators entering their environment and responding with appropriate defense mechanisms like releasing toxins or changing colors.
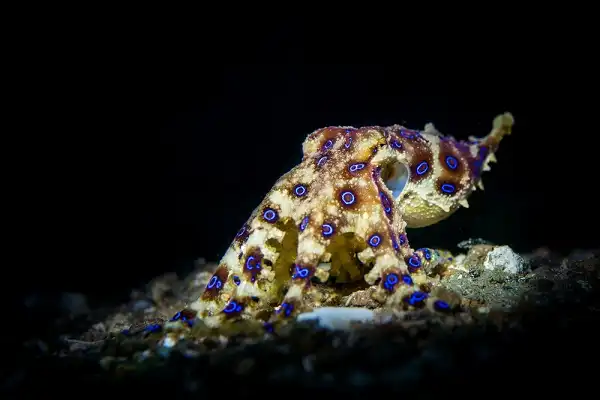

Blue-Ringed Octopus Speed
The Blue-Ringed Octopus is a surprisingly swift creature that can move swiftly through the water with the help of its siphon, a tube-like organ used to propel itself forward. With the help of its siphon and arms, this octopus can reach speeds of up to 1.2 m/s (2.6 mph). This impressive top speed helps it outmaneuver predators as well as catch prey such as small fish, crabs, and shrimp. However, what makes this octopus particularly unique is its ability to adapt its speed depending on the situation; when in an open space or when trying to escape from a predator, it can reach speeds of up to 2 m/s (4.5 mph) but when hunting or foraging, these creatures take their time and swim at a much slower rate of 0.1 m/s (0.22 mph). This allows them to search for food more thoroughly without expending too much energy. The Blue-Ringed Octopus also has a special type of muscle called ‘Erector musculature’ which helps it move faster than other octopuses by compressing the muscle fibers in order to achieve higher speeds over short distances. By using this specialized muscle tissue they can jump short distances and catch their prey before they have time to react!
Blue-Ringed Octopus Hunting
The Blue-Ringed Octopus is an impressive hunter, utilizing a wide variety of techniques to capture their prey. Firstly, they are outfitted with eight powerful suction cups on each of their tentacles which they use to latch onto and seize unsuspecting invertebrates such as crabs and sea snails. Additionally, these animals have been observed using tools such as shells and rocks to break open the hard outer shell of their prey – a behavior that is incredibly rare among octopuses! In addition to these physical techniques, Blue-Ringed Octopuses also possess an impressive array of specialized hunting strategies. The Blue-Ringed Octopus also utilizes camouflage as an effective hunting strategy; many species boast intricately patterned skin that helps them blend into their surroundings acting as an excellent form of protection from predators and assistance when hunting for food. When motionless, these creatures can be incredibly difficult for humans and animals alike to spot – giving them an advantage over potential prey! Finally, Blue-Ringed Octopuses possess powerful chemical sensors which allow them to detect potential prey even from long distances away by detecting chemical cues in the surrounding environment; this highly sophisticated sense gives them yet another edge when pursuing meals!
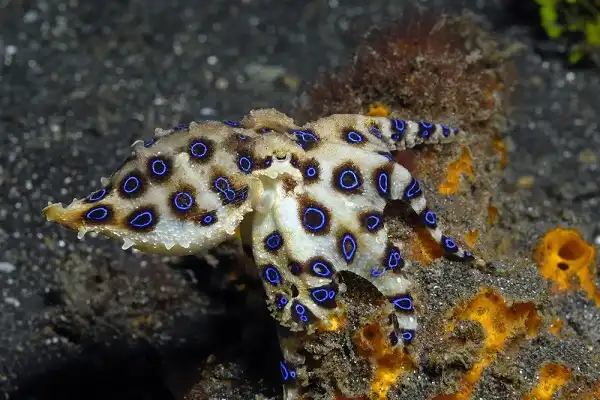

Conclusion
The Blue-Ringed Octopus is an incredibly intelligent and adaptable creature that showcases some remarkable hunting strategies. Whether it be using powerful suction cups to latch onto unsuspecting prey, utilizing camouflage for protection, or detecting chemical cues from long distances away – the octopus demonstrates impressive levels of skill and agility when hunting! This highly specialized form of behavior allows them to maximize efficiency when pursuing meals and ensure their own survival in a hostile marine environment. All in all, the Blue-Ringed Octopus is one of nature’s most impressive aquatic animals with intelligence rivaling even our own!
Frequently Asked Question

